DECLARE @TableName sysname SET @TableName = 'TableName' SELECT SUM(row_count) AS [RowCount] FROM sys.dm_db_partition_stats WHERE object_id=OBJECT_ID(@TableName) AND (index_id=0 or index_id=1);
Wednesday, March 9, 2016
Get Fast Rowcount
Thursday, March 3, 2016
Script - Email on Job Completion
-- ===============================================
-- Author: Eric Zierdt
-- Create date: 3/3/2016
-- Description: Emails upon agent job completion
-- ===============================================
DECLARE @JOB_NAME SYSNAME = N'AdventureWorks Backup'; -- NAME OF AGENT JOB
WHILE EXISTS
(
SELECT 1
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view job
JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobactivity activity ON job.job_id = activity.job_id
JOIN msdb.dbo.syssessions session ON session.session_id = activity.session_id
JOIN (
SELECT MAX(agent_start_date) AS max_agent_start_date
FROM msdb.dbo.syssessions
) session_max ON session.agent_start_date = session_max.max_agent_start_date
WHERE activity.run_Requested_date IS NOT NULL
AND activity.stop_execution_date IS NULL
AND job.name = @JOB_NAME
--AND activity.start_execution_date > CAST(GETDATE() AS DATE)
)
BEGIN
WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:45'; -- SET HOW OFTEN YOU WANT YOUR JOB TO CHECK
END
DECLARE @buffer_memory_used_MB FLOAT
,@Body VARCHAR(MAX)
,@Subject VARCHAR(255) = 'Job Complete'
,@To VARCHAR(512) = 'user@email.com' -- INSERT YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS HERE
SET @Body = 'The monitored job has completed running.'
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@recipients = @To
, @subject = @Subject
, @body = @Body
, @body_format = 'HTML'
Tuesday, December 10, 2013
Review of SQL Elements by Idera
Idera SQL Elements Review
I work for a large company which has well over 600 instances of SQL Server installed; we are constantly adding instances to our inventory. Managing our portfolio of instances is a challenge and to help ourselves out we created a series of tables which store server/instance information. Daily an SSIS job and Powershell scripts interrogate the various instances to collect basic information about them, like number/name of databases, disk size, up/down status, backup information, etc. We have been looking for a commercial solution to manage this for us and give us more options for a few years, but unable to find such a product.
Two months ago I was contacted by an Idera sales person who was interested in finding out if I was interested in one of their fine products and while we were talking, I told him what we were looking for in an inventory tool and asked him if they had a tool that would fit our needs. I expected to find out that they didn’t have anything and that what I wanted was a CMDB (configuration management database) solution; however that isn’t what he told me. He told me that Idera was going to debut a new solution called SQL Elements at PASS Summit that would do exactly what we needed and told me to sign up for the Beta program. I was a bit skeptical at first, but I signed up for the Beta program and hoped for the best.
My first impression was a bit of uncertainty, upon signing up for the Beta, I was placed on a wait list until I could be approved, I was afraid this might take a while and so I tried to get as much information off the Idera website as I could about the product. I had limited success finding anything about the product, which I’m sure was because as a beta product they didn’t have as much information to put out, I tried to sign up for a webcast, but had issues with that as well. After only a few days of waiting I was approved for the Beta and given access to the Beta Feedback system.
I dusted off my SQL Server 2012 evaluation VM and installed the product which was very simple. A few short minutes later I had a webpage up which was asking for my login, I found out that the system uses AD credentials to log in and as the person who installed it, mine were pre-setup in the system. I logged in and was given some basic instructions and asked to enter a list of instances to start monitoring. The process was pretty easy, you can enter a list of instances by separating them with a semicolon. Next you are asked for what credentials to use to connect to them. If you used a global AD group or user account on all your instances, this is easy if you setup Elements with that account; it will use the default account. Next you can enter some specific information on the instance, such as Owner, Location, comments and choose to assign a series of tags (I used the following tags: Production, Development, Test, DR). Once you confirm your request, Elements will start investigating the instances and reporting back on health checks and other basic Instance information. Overall the interface is pretty simple. The system has three main sections, a Dashboard view, the Explorer View and the Instance View. The Dashboard is a simple page showing how many of your monitored instances are up/down, Health Check Recommendations, Top Databases by Size, and Environment Statistics.

The Explorer View allows you to gather some information about your environment based on some filters. You can see Instance Count, DB Count, DB Size, Log Size and Activity information all correlated by either Instance, Owner, Location, Version, Database or by a custom Tag. You can filter the results by these last few options as well. So if you only want to see DB Size for Instances in Location X, you can do that.
The Instances View allows you to manage the instances you are monitoring. It allows you to add new instances by typing in the name(s) of the instances, or by seeing SQL Instances Elements has “Discovered” for you. Note that at the time of this writing, it appears that Elements can only detect SQL Server Instances in the subnet that it is installed in; they say they are working on it. The Instance view reports on Status, Response Time, Version, Edition, # of DBs, Size of DBs, Owner (manually entered), Location (manually entered), and if Clustered. The Discovery feature is nice, because it will let you stay up to date on any new instances which have been added to your environment
If you edit an instance, you get a wealth of information about it, like Database Names and Sizes, Max/Min Memory, Configuration Settings, and Server info (Drive sizes, VM, CPUs, Memory, OS, etc).
Under the hood, the database storing all this information is intuitive, the table names make sense, PK/FKs have been created, and a Database Diagram was easy to create. I was able to write a few SSRS reports against it pretty easily, allowing for me to fully utilize the data.
The Beta feedback and support website was very fun to use. You are given a certain number of “Votes” to use when submitting an issue or request. You can vote up other request on the system and by doing this, the developers know what is most important to their users. I found they were fairly responsive to acknowledging my request.
The software is licensed based on how many Instances you want to manage and they have an All you can Eat option, allowing you to license your entire environment and add new instances as they come online for a reasonable price. One important note is that this software only works with Instances of SQL Server which are 2005+, so if you have SQL Server 2000 instances in your environment, you will need to manage them through a separate method.
For companies with a larger SQL Server foot print or with less control on who can install SQL Server, this tool should be very attractive, it does a great job of helping you track your inventory and I’m sure as the product matures it will provide more and more functionality (growth tracking?). If on the other hand you have a smaller environment (< 15 SQL Instances), this may not offer you as much value.
Tuesday, August 20, 2013
PowerShell Progress Meter
In many of my past PowerShell scripts, I've included my own home-spun progress report in the results window. I like that a lot, but my mind was blown when I noticed that there is a "Write-Process" cmdlet...with some re-tweaking I made it rock and much more efficient.
So the situation where you would want to use this is if you are looping over a large dataset and it takes a while to bring back results (I often will use PowerShell to hit all the servers I control, get some information about them and return it to me (backup status, if they are VM's, configuration info, etc). It can take 20+ minutes to get to all the servers and it is nice to know how far along the process is; thats where this comes in handy.
Some things to keep in mind...You need to have some resultset to work with, it doesn't have to be a query, but it does have to be some kind of System.Array. After you generate the Array, run this bit of code...I'm calling my array "results":
<################################ ## SETUP PROGRESS VARIABLES ## ################################> $ResultsLen = $results.Length $LastPercentComplete = 0 [datetime]$DateStart = Get-Date -format G
This sets up some of the variables we will need inside the progress meter. Next, just after you issue your "foreach ($result in $results) {" You run the following code:
<##########################
## RUN PROGRESS METER ##
##########################>
foreach ($result in $results)
{
$currentRow++
$PercentComplete = [math]::floor(($CurrentRow/$ResultsLen)*100)
[datetime]$DateNow = Get-Date -format G
$diff = $DateNow-$DateStart
$DiffSeconds = $diff.TotalSeconds
$SecondsPerRecord = $DiffSeconds/$currentRow
$RemainingSeconds = $SecondsPerRecord*($ResultsLen-$currentRow)
$SecondsPerRecord = [Math]::Round($SecondsPerRecord,2)
Write-Progress -Activity "Investigating Servers..." `
-PercentComplete $PercentComplete `
-SecondsRemaining $RemainingSeconds `
-CurrentOperation "Current Row: $currentRow / $ResultsLen. Seconds/Record: $SecondsPerRecord Run Time (seconds): $DiffSeconds" `
-Status "Please wait."
Remove-Variable DateNow
Remove-Variable DiffSeconds
Remove-Variable SecondsPerRecord
Remove-Variable RemainingSeconds
}
You don't need to remove your variables, I just like to do it to clean up my code, I do this at the bottom of the script:
Remove-Variable ResultsLen Remove-Variable currentRow Remove-Variable LastPercentComplete Remove-Variable DateStart
Want to see it in action? Take my script and add this to the top of it (creates an array with 10000 items, which should keep the status bar up long enough for you to see):
$results = 1..10000
This looks awesome in PowerGUI, which is what I use for PowerShell Development, it looks a bit funky in the native PS window, but good enough to get you the idea. If you aren't using PowerGUI, give it a shot, it's free. http://www.powergui.org
As always, please leave comments below if you find this useful or have other suggestions. It's nice to know people read these posts.
Thursday, May 23, 2013
LEFT vs RIGHT vs SUBSTRING
DECLARE @Alpha VARCHAR(26)
SET @Alpha = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
SELECT @Alpha AS Alpha -- Display All characters
, LEFT(@Alpha,5) AS [LEFT(Alpha,5)] -- Display the first 5 characters from the Left
, RIGHT(@Alpha, 5) AS [RIGHT(Alpha,5)] -- Display the first 5 characters from the Right
, SUBSTRING(@Alpha, 15,5) AS [SUBSTRING(Alpha,15,5)] -- Display 5 characters staring at postition 15
, SUBSTRING(@Alpha, CHARINDEX('L',@Alpha),5) AS [SUBSTRING(Alpha, CHARINDEX('L',Alpha),5)] -- Display 5 characters Starting at "L"
, RIGHT(@Alpha, CHARINDEX('R',REVERSE(@Alpha))) AS [RIGHT(Alpha, CHARINDEX('R',REVERSE(Alpha)))] -- Display all Characters starting at the last "R" in the string
I added two additional results to this; the first uses SUBSTRING to return 5 characters, but rather than starting at a position, it uses CHARINDEX() to start at the first occurrence of a given string ("L" in the example above).
The second extra result uses the REVERSE() function to start on the right of the string and display all characters back to the first (or last depending on how you look at it) occurrence of a string or character ("R" in my example above). This would be beneficial if you had a windows path to something and you wanted to strip out the file name...say you had the path "c:\Folder1\Folder2\Folder3\Folder4\Folder5\File.ext" All you want is File.ext, so you could write:
RIGHT(@Path, CHARINDEX('\',REVERSE(@Path))).
Hope that helps someone out...if you found this useful, please post a comment below, and feel free to subscribe or follow me on twitter: @EricZierdt
Thursday, April 25, 2013
PowerShell - Check Backups
$LookupServer = New-Object -TypeName Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server -ArgumentList localhost
<###############################################
## VARIABLES TO ENTER: ##
## LooupServer: Server\Instance to check ##
###############################################>
$LookupServer = "localhost\DEV"
<###################################
## FUNCTION TO CHECK JOB STATUS ##
###################################>
Function Get-SQLJobStatus
{
param ([string]$server)
# Load SMO assembly, and if we're running SQL 2008 DLLs load the SMOExtended and SQLWMIManagement libraries
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('Microsoft.SqlServer.SMO') | out-null
# Create object to connect to SQL Instance
$srv = New-Object "Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server" $server
# used to allow piping of more than one job name to function
$srv.JobServer.Jobs | where {$_.Name -match "Backup" -and $_.Name -notmatch "LOG" -and $_.Name -notmatch "System" -and $_.IsEnabled -eq "True" -and $_.Name -notmatch "Optimizations" -and $_.Name -notmatch "History" -and $_.HasSchedule -eq "True"} | Select Name, CurrentRunStatus, LastRunOutcome,LastRunDate | Out-GridView
Remove-Variable srv
Remove-Variable server
}
<#############################################
## FUNCTION TO GET SERVER VERSION/EDITION ##
#############################################>
Function Get-SQLServerVersion
{
param ([string]$server)
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('Microsoft.SqlServer.SMO') | out-null
# Create object to connect to SQL Instance
$srv = New-Object "Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server" $server
$EditionName = $srv.Edition
##$srv.Version.Major
##$srv.VersionMinor
switch ($srv.Version.Major)
{
8 {$VersionName = "2000"}
9 {$VersionName = "2005"}
10 {$VersionName = "2008"}
11 {$VersionName = "2012"}
default {$VersionName = "The version could not be determined."}
}
if ($srv.Version.Major -eq "10")
{
if ($srv.VersionMinor -eq "50")
{
$VersionName += " R2"
}
}
$VersionEditionName = "$VersionName $EditionName"
$table = New-Object system.Data.DataTable "$TableName"
$col1 = New-Object system.Data.DataColumn VersionName,([string])
$col2 = New-Object system.Data.DataColumn VersionEditionName,([string])
$table.columns.add($col1)
$table.columns.add($col2)
$row = $table.NewRow();
$row.VersionName = $VersionName ;
$row.VersionEditionName = $VersionEditionName ;
$table.Rows.Add($row)
$table
Remove-Variable srv
Remove-Variable server
Remove-Variable EditionName
Remove-Variable VersionName
Remove-Variable VersionEditionName
Remove-Variable table
Remove-Variable col1
Remove-Variable col2
Remove-Variable row
}
CLS
$sd = Get-Date -format g
Write-Host "Starting: " $sd
Write-Host ""
$ServerInfo = Get-SQLServerVersion -server $LookupServer
$ServerVersionEdition = $ServerInfo.VersionEditionName
Write-Host "starting query for server: $LookupServer version: $ServerVersionEdition "
if ($ServerInfo.VersionName -eq "2000")
{
$BackupQuery = "
SELECT '$($result.InstanceName)' AS [Server], DBS.name AS DBName,ISNULL(BKS.backup_size,0) AS backup_size,ISNULL(BKS.backup_size,0) AS compressed_backup_size
,ISNULL(BCKFMLY.device_type,0) AS device_type,BKS.backup_start_date,BKS.backup_finish_date
, GETDATE() AS DateChecked, DATEDIFF(hour, BKUP.LastBackupDate, GETDATE()) AS HoursSinceLastBackup
FROM sysdatabases DBS
LEFT JOIN (
SELECT '$($result.InstanceName)' AS [server]
,BK.database_name AS DBName
,MAX(BK.backup_finish_date) AS LastBackupDate
,GETDATE() AS DateChecked
FROM msdb.dbo.backupset BK
LEFT JOIN msdb..backupmediafamily LBCKFMLY ON BK.media_set_id = LBCKFMLY.media_set_id
WHERE BK.[type] = 'D'
AND ISNULL(LBCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') LIKE '%\%'
AND ISNULL(LBCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') NOT LIKE '{%'
GROUP BY database_name
) BKUP ON BKUP.DBName = DBS.name
LEFT JOIN msdb.dbo.backupset BKS ON DBS.name = BKS.database_name AND BKUP.LastBackupDate = BKS.backup_finish_date AND BKS.[type] = 'D'
LEFT JOIN msdb..backupmediafamily BCKFMLY ON BKS.media_set_id = BCKFMLY.media_set_id
WHERE DBS.crdate < DATEADD(hour,-24,GETDATE())
AND DBS.name NOT IN ('tempdb')
AND DATABASEPROPERTYEX(DBS.name, 'Status') = 'ONLINE'
AND ISNULL(BCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') NOT LIKE '{%'
AND ISNULL(BCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') LIKE '%\%'
ORDER BY bkup.DBName
"
}
elseif ($ServerInfo.VersionName -eq "2005")
{
$BackupQuery = "
SELECT '$($result.InstanceName)' AS [Server], DBS.name AS DBName,ISNULL(BKS.backup_size,0) AS backup_size,ISNULL(BKS.backup_size,0) AS compressed_backup_size
,ISNULL(BCKFMLY.device_type,0) AS device_type,BKS.backup_start_date,BKS.backup_finish_date
, GETDATE() AS DateChecked, DATEDIFF(hour, BKUP.LastBackupDate, GETDATE()) AS HoursSinceLastBackup
FROM sys.databases DBS
OUTER APPLY (
SELECT BK.database_name ,
MAX(BK.backup_finish_date) AS LastBackupDate
FROM msdb.dbo.backupset BK
LEFT JOIN msdb..backupmediafamily LBCKFMLY ON BK.media_set_id = LBCKFMLY.media_set_id
WHERE DBS.name = BK.database_name
AND BK.[type] = 'D'
AND ISNULL(LBCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') LIKE '%\%'
AND ISNULL(LBCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') NOT LIKE '{%'
GROUP BY BK.database_name
) AS BKUP
LEFT JOIN msdb.dbo.backupset BKS ON BKUP.database_name = BKS.database_name AND BKUP.LastBackupDate = BKS.backup_finish_date AND BKS.[type] = 'D'
LEFT JOIN msdb..backupmediafamily BCKFMLY ON BKS.media_set_id = BCKFMLY.media_set_id
WHERE DBS.create_date < DATEADD(hour,-24,GETDATE())
AND DBS.state_desc = 'ONLINE'
AND DBS.name NOT IN ('tempdb')
AND ISNULL(BCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') NOT LIKE '{%'
AND ISNULL(BCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') LIKE '%\%'
ORDER BY DBS.name
"
}
else
{
$BackupQuery = "
SELECT '$($result.InstanceName)' AS [Server], DBS.name AS DBName,ISNULL(BKS.backup_size,0) AS backup_size,ISNULL(BKS.backup_size,0) AS compressed_backup_size
,ISNULL(BCKFMLY.device_type,0) AS device_type,BKS.backup_start_date,BKS.backup_finish_date
, GETDATE() AS DateChecked, DATEDIFF(hour, BKUP.LastBackupDate, GETDATE()) AS HoursSinceLastBackup
FROM sys.databases DBS
OUTER APPLY (
SELECT BK.database_name ,
MAX(BK.backup_finish_date) AS LastBackupDate
FROM msdb.dbo.backupset BK
LEFT JOIN msdb..backupmediafamily LBCKFMLY ON BK.media_set_id = LBCKFMLY.media_set_id
WHERE DBS.name = BK.database_name
AND BK.[type] = 'D'
AND ISNULL(LBCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') LIKE '%\%'
AND ISNULL(LBCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') NOT LIKE '{%'
GROUP BY BK.database_name
) AS BKUP
LEFT JOIN msdb.dbo.backupset BKS ON BKUP.database_name = BKS.database_name AND BKUP.LastBackupDate = BKS.backup_finish_date AND BKS.[type] = 'D'
LEFT JOIN msdb..backupmediafamily BCKFMLY ON BKS.media_set_id = BCKFMLY.media_set_id
WHERE DBS.create_date < DATEADD(hour,-24,GETDATE())
AND DBS.state_desc = 'ONLINE'
AND DBS.name NOT IN ('tempdb')
AND ISNULL(BCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') NOT LIKE '{%'
AND ISNULL(BCKFMLY.physical_device_name,'\') LIKE '%\%'
ORDER BY DBS.name
"
}
try
{
Get-SQLJobStatus -server $LookupServer
$BackupResults = Invoke-Sqlcmd -Query $BackupQuery -ServerInstance $LookupServer -Database master -ErrorAction Stop;
$BackupResults | Out-GridView
Remove-Variable BackupResults
Remove-Variable BackupQuery
}
catch
{
Write-OutputHighlighted -inputText "Error connecting to server " $LookupServer
}
$ed = Get-Date -format g
Write-Host "
Complete: " $ed
<#######################
## CLEANUP VARIABLES ##
#######################>
Remove-Variable sd
Remove-Variable ed
Remove-Variable LookupServer
Remove-Variable ServerInfo
Remove-Variable ServerVersionEdition
You can see that we have broken out the query to check msdb for last backup info into three different queries, based on if the server is 2000, 2005 or 2008+ This is done due to the differences in views with the different versions.
Wednesday, April 24, 2013
SQL Saturday 175 is this weekend!
Friday, April 19, 2013
SQL 2012 Extended Event Wizard Question
Here is my query (which works in 2012, if I simply execute it)
IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM sys.server_event_sessions WHERE name='MonitorExpensiveQuery')
DROP EVENT SESSION MonitorExpensiveQuery ON SERVER
GO
--Creating a Extended Event session with CREATE EVENT SESSION command
CREATE EVENT SESSION MonitorExpensiveQuery ON SERVER
ADD EVENT sqlserver.sql_statement_completed
(
ACTION
(
sqlserver.client_app_name
,sqlserver.client_hostname
,sqlserver.username
,sqlserver.nt_username
,sqlserver.session_id
,sqlserver.sql_text
)
WHERE (
duration > 3000000
OR cpu_time > 1000
OR reads > 10000
OR writes > 10000
)
)
,ADD EVENT sqlserver.sp_statement_completed
(
ACTION
(
sqlserver.client_app_name
,sqlserver.client_hostname
,sqlserver.username
,sqlserver.nt_username
,sqlserver.session_id
,sqlserver.sql_text
)
WHERE (
duration > 3000000
OR cpu_time > 1000
OR reads > 10000
OR writes > 10000
)
)
ADD TARGET package0.ring_buffer WITH (MAX_DISPATCH_LATENCY = 1 SECONDS, STARTUP_STATE = ON) -- The target
GO
ALTER EVENT SESSION MonitorExpensiveQuery ON SERVER STATE = START
GO
So I kick off the GUI and the first few pages seem pretty straight forward...Add my Session name:

But when I get to the Filter page, which I am guessing is the equivalent of the "WHERE" caluse, I don't see any of my fields (duration, cpu_time, reads or writes):

So I'm unsure how to properly set this up. Any help appreciated
Monday, October 1, 2012
SQL Saturday 149 Scripts and stuff
Hello everyone,
I had a great time meeting other SQL Server Professionals at SQL Saturday 149 in Minneapolis at the U of M campus, and chatting up with people afterwards at the after party. To those of you who attended my session on Execution Plans, I'd like to say thank you, I hope you took away some useful information; please feel free to email me directly with questions and please connect with me on LinkedIn. I also want to thank you for your feedback on my session; I appreciate the comments, suggestions and observations, it will help me better present in the future.
All the queries that I used in my presentation can be found here: http://ericemployed.blogspot.com/2011/11/sqlsaturday-99-scripts.html
Tuesday, August 28, 2012
SQL Saturday 149 Announcement
Monday, May 14, 2012
Extended Events with a view
USE [master] GO CREATE SCHEMA [XE] AUTHORIZATION [dbo] GOCreate the View (using the XQuery from my previous post:
USE [master]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
/************************************************************
* AUTHOR: Eric Zierdt *
* CREATED: 05/08/2012 *
* USAGE: SELECT * FROM [XE].[vw_Log_Shrink] *
************************************************************/
CREATE VIEW [XE].[vw_Log_Shrink]
AS
WITH Data
AS (
SELECT CAST(target_data AS XML) AS TargetData
FROM sys.dm_xe_session_targets dt
JOIN sys.dm_xe_sessions ds ON ds.address = dt.event_session_address
JOIN sys.server_event_sessions ss ON ds.Name = ss.Name
WHERE dt.target_name = 'ring_buffer'
AND ds.Name = 'XE_Log_Shrink'
)
SELECT DATEADD(hour,-5,XEventData.XEvent.value('(@timestamp)[1]', 'datetime')) AS event_timestamp
,XEventData.XEvent.value('@name', 'varchar(4000)') AS event_name
,DB_NAME(XEventData.XEvent.value('(data/value)[2]', 'VARCHAR(100)')) AS DatabaseName
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[2]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS client_hostname
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[3]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS nt_username
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[6]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS username
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[5]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS sql_text
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[4]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS session_id
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[1]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS client_app_name
FROM Data d
CROSS APPLY TargetData.nodes('//RingBufferTarget/event') AS XEventData ( XEvent )
GO
Thats all you have to do, now you can query this like a DMV, just write:
SELECT * FROM [XE].[vw_Log_Shrink] WHERE [event_timestamp] > '5/8/2012'Let me know your thoughts.
Friday, April 20, 2012
Extended Event - Check for Log Shrink and Email
First we need to create the Extended Event (hereafter referred to as XE) to capture the log shrink:
IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM sys.server_event_sessions WHERE name = 'XE_Log_Shrink')
DROP EVENT SESSION XE_Log_Shrink ON SERVER
GO
CREATE EVENT SESSION XE_Log_Shrink ON SERVER -- Session Name
ADD EVENT sqlserver.databases_log_shrink -- Event we want to capture
(
ACTION -- What contents to capture
(
sqlserver.client_app_name
,sqlserver.client_hostname
,sqlserver.nt_username
,sqlserver.session_id
,sqlserver.sql_text
,sqlserver.username
)
)
ADD TARGET package0.ring_buffer WITH (MAX_DISPATCH_LATENCY = 1 SECONDS, STARTUP_STATE = ON) -- The target
GO
ALTER EVENT SESSION XE_Log_Shrink ON SERVER STATE = START
Next to check it, we need to shrink a log (I'll auto grow it again, so I can redo this numerous times if I need to)
USE [AdventureWorks]
GO
DBCC SHRINKFILE (N'AdventureWorks_Log' , 1)
GO
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [AdventureWorks] MODIFY FILE ( NAME = N'AdventureWorks_Log', SIZE = 100MB )
GO
Lets check the XE to see if we captured the event:
;WITH Data
AS (
SELECT CAST(target_data AS XML) AS TargetData
FROM sys.dm_xe_session_targets dt
JOIN sys.dm_xe_sessions ds ON ds.address = dt.event_session_address
JOIN sys.server_event_sessions ss ON ds.Name = ss.Name
WHERE dt.target_name = 'ring_buffer'
AND ds.Name = 'XE_Log_Shrink'
)
SELECT DATEADD(hour,-5,XEventData.XEvent.value('(@timestamp)[1]', 'datetime')) AS event_timestamp
,XEventData.XEvent.value('@name', 'varchar(4000)') AS event_name
,DB_NAME(XEventData.XEvent.value('(data/value)[2]', 'VARCHAR(100)')) AS DatabaseName
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[2]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS client_hostname
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[3]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS nt_username
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[6]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS username
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[5]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS sql_text
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[4]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS session_id
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[1]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS client_app_name
FROM Data d
CROSS APPLY TargetData.nodes('//RingBufferTarget/event') AS XEventData ( XEvent )
So, we should see the event now. But lets take it a step further, lets say we want to get emailed when it happens. I've created this stored proc which will check once an hour (this is a variable, you can configure it as you see fit, but keep it under 2 hours or else you'll have to modify my waitfor logic...or you could remove the waitfor logic and just run it from the scheduler in the agent job you setup, just match up the @How_Often variable with how often your job fires)
USE master
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
-- ===========================================================
-- Author: Eric Zierdt
-- Create date: 4/19/2012
-- Description: Checks for Log Shrinkage and sends email
-- URL: http://ericemployed.blogspot.com
-- Usage: exec Email_On_Log_Shrinkage 60
-- ===========================================================
ALTER PROCEDURE Email_On_Log_Shrinkage
-- Add the parameters for the stored procedure here
@How_Often INT = 60
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON
Start_Code:
--DECLARE @How_Often INT = 60
DECLARE @RowCount INT = 0
,@SQL VARCHAR(MAX) = ''
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM tempdb.dbo.sysobjects WHERE ID = OBJECT_ID(N'tempdb..#TempData'))
BEGIN
DROP TABLE #TempData
END
;WITH Data
AS (
SELECT CAST(target_data AS XML) AS TargetData
FROM sys.dm_xe_session_targets dt
JOIN sys.dm_xe_sessions ds ON ds.address = dt.event_session_address
JOIN sys.server_event_sessions ss ON ds.Name = ss.Name
WHERE dt.target_name = 'ring_buffer'
AND ds.Name = 'XE_Log_Shrink'
)
SELECT DATEADD(hour,-5,XEventData.XEvent.value('(@timestamp)[1]', 'datetime')) AS event_timestamp
,XEventData.XEvent.value('@name', 'varchar(4000)') AS event_name
,DB_NAME(XEventData.XEvent.value('(data/value)[2]', 'VARCHAR(100)')) AS DatabaseName
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[2]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS client_hostname
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[3]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS nt_username
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[6]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS username
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[5]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS sql_text
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[4]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS session_id
,XEventData.XEvent.value('(action/value)[1]', 'VARCHAR(512)') AS client_app_name
INTO #TempData
FROM Data d
CROSS APPLY TargetData.nodes('//RingBufferTarget/event') AS XEventData ( XEvent )
WHERE DATEADD(hour,-5,XEventData.XEvent.value('(@timestamp)[1]', 'datetime')) > DATEADD(MINUTE,-1*@How_Often,GETDATE())
SELECT @RowCount = COUNT(1) FROM #TempData
IF @RowCount > 0
BEGIN
PRINT CAST(@RowCount AS VARCHAR(10)) + ' Log Shrink records were found'
SET @SQL = '
| Server | Database Name | Time Stamp | Client Hostname | Username | SQL_Text |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ' + @@SERVERNAME + ' | ' + @DBName + ' | ' + @TimeStamp + ' | ' + @HostName + ' | ' + @UserName + ' | ' + @SQL_Text + ' |
'
END
ELSE
PRINT 'No Shrinks in the time frame requested'
--PRINT @SQL
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@recipients = '[Your Email Here]',
@body = @SQL,
@subject = 'Log Shrink Detected',
@profile_name = '[Your Profile Name Here]',
@body_format = 'html';
DROP TABLE #TempData
DECLARE @Delay VARCHAR(10)
--,@How_Often INT = 60
IF @How_Often < 60
SET @Delay = '00:' + RIGHT('00' + CAST(@How_Often AS VARCHAR(2)),2) + ':00'
ELSE
SET @Delay = '01:' + RIGHT('00' + CAST(@How_Often-60 AS VARCHAR(2)),2) + ':00'
WAITFOR DELAY @Delay
GOTO Start_Code
END
GO
Then the last step is to call this proc from a agent job. Iif you use the WaitFor logic, I'd still set a schedule to run every hour, just in case it fails...but the more I think about this, the more I prefer not using the WaitFor logic and just running the job every hour; but if the job fails, you won't get emailed.
--Eric
Friday, April 13, 2012
SSRS Queries
One of the first things I wanted to know was what subscriptions had run that did not succeed. This query should be run on the server that hosts your ReportServer Database. I'm running these on SQL Server 2008R2
USE [ReportServer]
--GET THE SERVER NAME
DECLARE @ServerURL VARCHAR(MAX)
SELECT TOP 1 @ServerURL =[MachineName]
FROM [dbo].Keys
WHERE [MachineName] IS NOT NULL
IF CHARINDEX('\',@ServerURL) > 0
SET @ServerURL = LEFT(@ServerURL,CHARINDEX('\',@ServerURL)-1)
SET @ServerURL = 'http://' + @ServerURL + '/Reports/Pages'
--FIND THE NON-SUCCESSFUL SUBSCRIPTIONS
;WITH AgentJobsCTE AS (
SELECT [SJ].job_id
,[SJ].name AS AgentJobName
,[SJS].[command]
,CAST(REPLACE(REPLACE(REPLACE([SJS].[command],'exec [ReportServer].dbo.AddEvent @EventType=''TimedSubscription'', @EventData=''',''),'exec ReportServer.dbo.AddEvent @EventType=''TimedSubscription'', @EventData=''',''), '''', '') AS SYSNAME) AS SubscriptionID
FROM msdb.[dbo].[sysjobs] AS SJ
JOIN msdb.[dbo].[sysjobsteps] AS SJS ON [SJ].[job_id] = [SJS].[job_id]
WHERE SJS.[command] LIKE '%TimedSubscription%'
)
SELECT O.[UserName] AS OwnerName,M.[UserName] AS ModifiedBy,C.[Name] AS ReportName,[AJ].AgentJobName,S.[SubscriptionID],S.[LastStatus],S.[LastRunTime],S.[ModifiedDate],S.[Report_OID]
,@ServerURL + '/SubscriptionProperties.aspx?ItemPath=' + REPLACE(REPLACE(C.Path,'/','%2f'),' ','+') + '&IsDataDriven=False&SubscriptionID=' + CAST(S.[SubscriptionID] AS VARCHAR(MAX)) AS SubscriptionURL
,@ServerURL + '/Report.aspx?ItemPath=' + REPLACE(REPLACE(C.Path,'/','%2f'),' ','+') + '&SelectedTabId=PropertiesTab&SelectedSubTabId=SubscriptionsTab&SortBy=LastExecuted&IsAscending=false' AS ReportURL
FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[Subscriptions] AS S
JOIN [ReportServer].[dbo].[Users] AS O ON [S].[OwnerID] = [O].[UserID]
JOIN [ReportServer].[dbo].[Users] AS M ON S.[ModifiedByID] = [M].[UserID]
JOIN [ReportServer].[dbo].[Catalog] AS C ON [S].[Report_OID] = [C].[ItemID]
LEFT JOIN [AgentJobsCTE] AJ ON CAST(S.[SubscriptionID] AS SYSNAME) = AJ.[SubscriptionID]
WHERE [LastRunTime] >= '04/02/2012 15:00' --NOT NEEDED, BUT MAKES YOUR LIST SHORTER
AND [LastStatus] NOT LIKE 'Mail sent to%'
AND [LastStatus] NOT LIKE 'The file "%'
--AND [LastStatus] NOT LIKE 'Pending%' --Pending are currently running.
ORDER BY [LastRunTime] DESC
I noticed that I was seeing a number of subscriptions currently running for the same report, many run at the same time. I wrote a query to tell me which subscriptions had the same "report parameter values". This doesn't look at the subscription start time or days of the week, just the parameters...so you'll need to do some investigation (the next query will help with that)
USE [ReportServer]
DECLARE @ServerURL VARCHAR(MAX)
SELECT TOP 1 @ServerURL =[MachineName]
FROM [dbo].Keys
WHERE [MachineName] IS NOT NULL
IF CHARINDEX('\',@ServerURL) > 0
SET @ServerURL = LEFT(@ServerURL,CHARINDEX('\',@ServerURL)-1)
SET @ServerURL = 'http://' + @ServerURL + '/Reports/Pages'
;WITH DuplicateSubscriptions AS (
SELECT C.Name AS ReportName
,CAST(Parameters AS VARCHAR(MAX)) AS Parameters
,[Report_OID]
,C.Path
,COUNT(1) AS [Count]
FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[Subscriptions] S
JOIN [ReportServer].[dbo].[Catalog] AS C ON [S].[Report_OID] = [C].[ItemID]
LEFT JOIN [dbo].[ReportSchedule] AS RS ON [S].[SubscriptionID] = [RS].[SubscriptionID]
LEFT JOIN [dbo].[Schedule] AS SC ON RS.[ScheduleID] = SC.[ScheduleID]
WHERE (SC.EndDate IS NULL OR (SC.EndDate IS NULL AND SC.[RecurrenceType] <> 1))
GROUP BY CAST(Parameters AS VARCHAR(MAX)),[Report_OID],C.Name,C.Path
HAVING COUNT(1) > 1
)
SELECT *
,@ServerURL + '/Report.aspx?ItemPath=' + REPLACE(REPLACE(Path,'/','%2f'),' ','+') + '&SelectedTabId=PropertiesTab&SelectedSubTabId=SubscriptionsTab&SortBy=LastExecuted&IsAscending=false' AS URL
FROM [DuplicateSubscriptions]
--ORDER BY [ReportName], [Count] DESC
ORDER BY [Count] DESC, [ReportName]
So when you find a possible duplicate subscription in the previous list, get the Report_OID and Parameters field and past them into the variables in this query and execute to see if it needs more investigation. I usually look at the "LastRun" field and see if there are any duplicates in that list. If you need to dig in more, the query provides links to both the subscription webpage and the report management page listing all subscriptions
USE [ReportServer]
-- VIEW ALL (NON EXPIRED) SUBSCRIPTIONS FOR A SPECIFIC REPORT WITH SPECIFIC PARAMETERS
DECLARE @ServerSubscriptionURL VARCHAR(MAX)
SELECT TOP 1 @ServerSubscriptionURL =[MachineName]
FROM [dbo].Keys
WHERE [MachineName] IS NOT NULL
IF CHARINDEX('\',@ServerSubscriptionURL) > 0
SET @ServerSubscriptionURL = LEFT(@ServerSubscriptionURL,CHARINDEX('\',@ServerSubscriptionURL)-1)
SET @ServerSubscriptionURL = 'http://' + @ServerSubscriptionURL + '/Reports/Pages'
DECLARE @ReportID sysname = 'F9999999-888G-7H77-I9I9-000000J00000' -- ReportID from previous query
,@ParameterList VARCHAR(MAX) = '[parameters]'-- Parameters from previous query
SELECT C.Name AS ReportName
,S.[SubscriptionID]
,S.[Description] Descr
,S.[LastRunTime] LastRun
,S.[LastStatus]
--,SC.[EndDate]
--,SC.[RecurrenceType]
,U.[UserName] AS Owner
,@ServerSubscriptionURL + '/SubscriptionProperties.aspx?ItemPath=' + REPLACE(REPLACE(C.Path,'/','%2f'),' ','+') + '&IsDataDriven=False&SubscriptionID=' + CAST(S.[SubscriptionID] AS VARCHAR(MAX)) AS SubscriptionURL
,@ServerSubscriptionURL + '/Report.aspx?ItemPath=' + REPLACE(REPLACE(C.Path,'/','%2f'),' ','+') + '&SelectedTabId=PropertiesTab&SelectedSubTabId=SubscriptionsTab&SortBy=LastExecuted&IsAscending=false' AS ReportURL
FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[Subscriptions] S
JOIN [ReportServer].[dbo].[Users] AS U ON [S].[OwnerID] = [U].[UserID]
JOIN [ReportServer].[dbo].[Catalog] AS C ON [S].[Report_OID] = [C].[ItemID]
LEFT JOIN [dbo].[ReportSchedule] AS RS ON [S].[SubscriptionID] = [RS].[SubscriptionID]
LEFT JOIN [dbo].[Schedule] AS SC ON RS.[ScheduleID] = SC.[ScheduleID]
WHERE Report_OID = @ReportID
AND CAST(S.Parameters AS VARCHAR(MAX)) = @ParameterList
AND (SC.EndDate IS NULL OR (SC.EndDate IS NULL AND SC.[RecurrenceType] <> 1))
ORDER BY S.Description
But wait, thats not all, some additional interesting queries:
See all currently running reports
SELECT [JobID],[StartDate],[ComputerName],[RequestName],[RequestPath]
,[Description],[Timeout] AS Timeout, DATEDIFF(ss, startdate, GETDATE()) AS SecondsSinceRun
, DATEDIFF(mi, startdate, GETDATE()) AS MinutesSinceRun
,[JobAction],[JobType],[JobStatus]
,'http://[reporturl]/Reports/Pages/Report.aspx?ItemPath=' + REPLACE(REPLACE(RJ.RequestPath,'/','%2f'),' ','+') + '&SelectedTabId=PropertiesTab&SelectedSubTabId=SubscriptionsTab&SortBy=LastExecuted&IsAscending=false' AS ReportURL
FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[RunningJobs] AS RJ
See the run information for a specific report (comment out the RequestType if you want to see things other than subscriptions)
SELECT *
FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLog2] AS EL
WHERE [ReportPath] LIKE '%[report name=""]' AND [RequestType] = 'Subscription'
ORDER BY [TimeStart] DESC
View a schedule for a specific Subscription
-- VIEW SCHDULE DATA FOR A SPEICIFC SUBSCRIPTION
SELECT *
FROM [dbo].[Schedule] AS S
JOIN [dbo].[ReportSchedule] AS RS ON [S].[ScheduleID] = [RS].[ScheduleID]
WHERE RS.[SubscriptionID] = '[subscriptionid]'
Ok, one last one, this lets you see all expired (past the end date) and one time subscriptions (useful if you want to clean them up)
-- EXPIRED AND ONE TIME RUN SUBSCRIPTIONS
DECLARE @ServerURL VARCHAR(MAX)
SELECT TOP 1 @ServerURL =[MachineName]
FROM [dbo].Keys
WHERE [MachineName] IS NOT NULL
IF CHARINDEX('\',@ServerURL) > 0
SET @ServerURL = LEFT(@ServerURL,CHARINDEX('\',@ServerURL)-1)
SET @ServerURL = 'http://' + @ServerURL + '/Reports/Pages'
;WITH ExpiredSubscriptions AS
(
SELECT RS.[SubscriptionID], S.[EndDate]
FROM [dbo].[Schedule] AS S
JOIN [dbo].[ReportSchedule] AS RS ON [S].[ScheduleID] = [RS].[ScheduleID]
WHERE S.[EndDate] < GETDATE() OR S.[RecurrenceType] = 1
)
SELECT S.[SubscriptionID]
,C.Name AS ReportName
,S.[Description] Descr
,S.[LastRunTime] LastRun
,ES.[EndDate]
,S.[LastStatus]
,U.[UserName] AS Owner
,@ServerURL + '/SubscriptionProperties.aspx?ItemPath=' + REPLACE(REPLACE(Path,'/','%2f'),' ','+') + '&IsDataDriven=False&SubscriptionID=' + CAST(S.[SubscriptionID] AS VARCHAR(MAX)) AS SubscriptionURL
,@ServerURL + '/Report.aspx?ItemPath=' + REPLACE(REPLACE(Path,'/','%2f'),' ','+') + '&SelectedTabId=PropertiesTab&SelectedSubTabId=SubscriptionsTab&SortBy=LastExecuted&IsAscending=false' AS ReportURL
FROM Subscriptions S
JOIN [dbo].[Users] AS U ON [S].[OwnerID] = [U].[UserID]
JOIN [ReportServer].[dbo].[Catalog] AS C ON [S].[Report_OID] = [C].[ItemID]
JOIN [ExpiredSubscriptions] ES ON S.[SubscriptionID] = ES.[SubscriptionID]
ORDER BY C.[Name], ES.[EndDate] DESC
If you have any other good queries, please drop them in a comment below
Saturday, November 12, 2011
SQLSaturday #99 Scripts
What are Execution Plans?
The definition I used in my presentation was:
"In simplest terms, Execution Plans are the steps that SQL Server takes in order to return the requested information."
How do I see Execution Plans
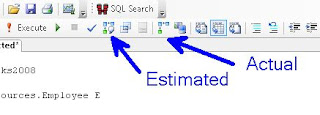
For Graphical Execution Plans there are a few ways:
In the Menu Bar choose Query and you can choose either Display Estimated Execution Plan or Include Actual Execution Plan.
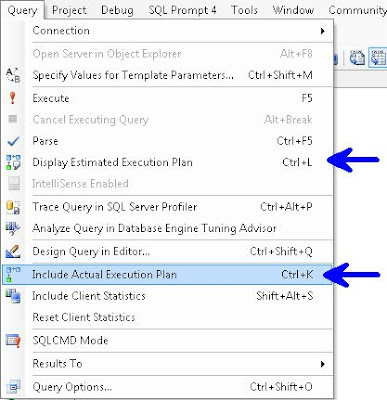
Right Click Query Window
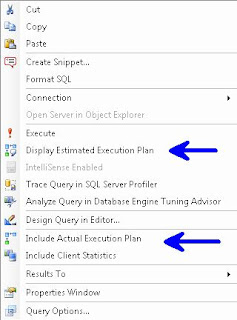
Control L (Estimated) / M (Actual)
Or the simplest way, use the two buttons
Plan Type
Graphical, Text, XML
Gets more difficult to read as you go from left to right, but also get more info. i.e. Graphical is easier to read than is Text, which is easier to read than XML, but XML gives more info than Text, which in turn gives more info than Graphical.
Note: I've read that Microsoft is planning on deprecating Text Execution Plan
Permission
sysadmin, dbcreator or db_owner, or be granted the ShowPlan permission:
GRANT SHOWPLAN TO [username]
Reuse
The Optimizer stores plans so it can reuse them, this is removed on server restart or DBCC FREEPROCCACHE
The examples below use AdventureWorks and AdventureWorks2008, available at CodePlex
To start, please turn on Include Actual Execution Plan from any of the above described methods. Next run this query:
/* QUERY 1 */
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT *
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
In your results window, you will see a new tab called "Execution Plan", if you click on that, you should see the following. Hovering over the left most object will display the tool tip in this screenshot:
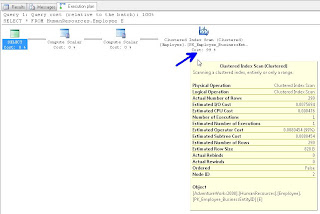
If you right click on any of the objects in this window you can choose Properties and get additional info. I traditionally read from right to left, but you can get important info like "Optimization Level" if you get the properties from the left most (select) object. The most common Optimization Levels are Trivial or Full. This is a trivial plan because there are no where clauses or joins, so the Optimizer can only get this data one way, doing a full table scan.
We discussed the difference between A Scan and a Seek. A Scan means that SQL Server needed to look at every record in the table, where as a Seek means that it can use an index to go directly to the record in question. We likened this to a phone book, if you are looking for the phone number and address for "Sam Smith", a Scan means you have to look at every page and every record even after it already finds a record for Sam Smith, whereas a Seek can go right to the S's at the top of the page and quickly go to the Sam Smith record and stop looking.
We discussed how typically, a scan performs worse than a seek. However if the table is small, and in some other instances, a Scan can be the best option.
Next we ran the following query:
/* QUERY 2 */
USE AdventureWorks
SELECT E.Title
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
WHERE E.EmployeeID = 185
And we saw an Clustered Index Seek this time.

Our next query:
/* QUERY 3 */
USE AdventureWorks
SELECT MiddleName
FROM Person.Contact
WHERE Phone LIKE '11%'
Showed us the "Missing Index" at the top of the Execution Plan
You can right click on this "Missing Index" text and "Missing Index Details" to have it open the suggested index in a new window.
We altered the index slightly (gave it a name and the WITH(Data_Compression=ROW) hint) and ran this:
USE [AdventureWorks]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [Contact_IX_Phone] ON [Person].[Contact]
(
[Phone]
)
INCLUDE
(
[MiddleName]
)
WITH(Data_Compression=ROW)
GO
We then re-ran Query 3 and saw that we now have an Index Seek.
For Query 4 we ran:
/* QUERY 4 */
USE AdventureWorks
SELECT E.Title
,C.FirstName
,C.LastName
,M.FirstName AS ManagerFirstName
,M.LastName AS ManagerLastName
,E.ManagerID
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
JOIN Person.Contact C ON E.ContactID = C.ContactID
JOIN Person.Contact M ON E.ManagerID = M.ContactID
WHERE E.ManagerID = 109
AND EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM Person.Contact AS C2
WHERE E.ContactID = C2.ContactID
)
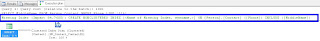
Which showed us a Clustered Index Scan on HumanResources.Employee
It didn't state a missing index so we discussed how to come up with our own index.
We started by noticing that ContactID and ManagerID were both being Joined, and that ManagerID was in the WHERE clause, so we created an index on that, also we used INCLUDE (Title) because Title was in the select List:
USE [AdventureWorks]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [HR-Employee_IX_EZ1] ON [HumanResources].[Employee]
(
[ContactID] ASC, [ManagerID] ASC
)
INCLUDE ( [Title])
WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF, ONLINE = ON, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION=ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
We did discuss some of the WITH parts, like the use of ONLINE = ON as a hint to try to make this index without causing any locking if possible.
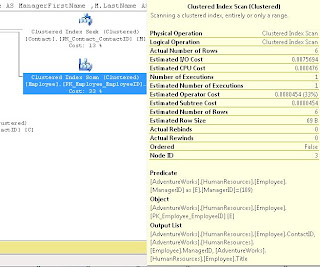
After we ran this, we noted that the Index Scan still existed; we discussed that because the ContactID wasn't part of the WHERE, it should go in the INCLUDE. After making this change and re-running the index we saw it change to a Index Seek (note I'm using the DROP_EXISTING = ON here rather than the DROP statement I used in class).
USE [AdventureWorks]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [HR-Employee_IX_EZ1] ON [HumanResources].[Employee]
(
[ManagerID] ASC
)
INCLUDE ( [ContactID], [Title])
WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = ON, ONLINE = ON, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION=ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
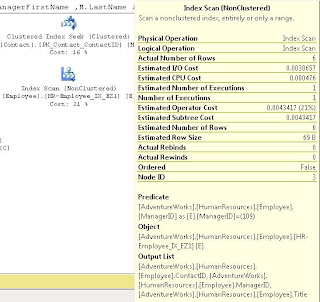
We noted that the when we hover over the Employee object in the above screen shots, that it the Estimated I/O Cost dropped from 0.0075 to 0.00386 after we converted from a SCAN to a SEEK and the Estimated Operator Cost changed from .008 to .004 We acknowledged that these numbers seem small, but if this table explodes and becomes very large, we would expect to see these go up and seeing the costs cut in half is a good thing.
For Query 5 we let the audience try to determine what was wrong and needed to be changed:
/* QUERY 5 */
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT SOH.AccountNumber
,S.Name AS StoreName
,SOH.OrderDate
,P.Name AS ProductName
,SOD.OrderQty
,SOD.UnitPrice
,SOD.LineTotal
FROM Sales.SalesOrderHeader SOH
JOIN Sales.SalesOrderDetail SOD ON SOH.SalesOrderID = SOD.SalesOrderID
JOIN Sales.Customer C ON SOH.CustomerID = C.CustomerID
JOIN Sales.Store S ON C.StoreID = S.BusinessEntityID
JOIN Production.Product P ON SOD.ProductID = P.ProductID
We had a big Execution Plan, we discussed that you can click on the [+] symbol at the bottom left of the window to help scroll around:
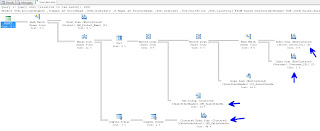
We all agreed that the Index Scan's had to go. We also introduced the "Key Lookup" object. I discussed how Key Lookups are not good, and indicate that the Optimizer couldn't get the key from the index. After looking at the query, we decided to add a number of indexes:
USE [AdventureWorks2008]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [SalesOrderHeader_I01] ON [Sales].[SalesOrderHeader]
(
[SalesOrderID] ASC,
[CustomerID] ASC
)
INCLUDE
(
AccountNumber
,OrderDate
)
WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF, ONLINE = OFF
, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
USE [AdventureWorks2008]
GO
/****** Object: Index [AK_SalesOrderDetail_rowguid] Script Date: 09/23/2011 14:35:47 ******/
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [SalesOrderDetail_I01] ON [Sales].[SalesOrderDetail]
(
SalesOrderID ASC
)
INCLUDE
(
ProductID
, OrderQty
,UnitPrice
,LineTotal
)
WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF
, ONLINE = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
USE [AdventureWorks2008]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [Customer_I01] ON [Sales].[Customer]
(
[CustomerID] ASC)
INCLUDE (
[StoreID]
)WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF, ONLINE = OFF
, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
USE [AdventureWorks2008]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [Store_I01] ON [Sales].[Store]
(
[BusinessEntityID] ASC
)
INCLUDE
(
Name
)
WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF, ONLINE = OFF
, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
This did seem to help, when we compared the Estimated I/O's and CPU's but we still were seeing SCANS.
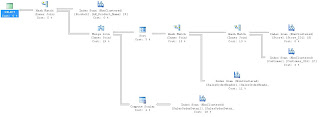
We scratched our heads and then realized that we didn't have a WHERE clause, so we were pulling every record possible. We added:
WHERE SOH.SalesOrderID = 22
and our Execution Plan looked much, much better.
By this time, I think you can figure out what needs to be done for Query 6:
/* QUERY 6 */
SELECT LineTotal, OrderQty
FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail s
JOIN Production.Product p ON s.ProductID = p.ProductID
WHERE CarrierTrackingNumber = '4911-403C-98'
Next I showed this query which returns all the Cached plans that SQL Server has ready to go:
SELECT [cp].[refcounts]
, [cp].[usecounts]
, [cp].[objtype]
, [st].[dbid]
, [st].[objectid]
, [st].[text]
, [qp].[query_plan]
FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans cp
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text ( cp.plan_handle ) st
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan ( cp.plan_handle ) qp ;
Then we moved on to looking at Execution Plans returned as Text (Note remember to turn off "Include Actual Execution Plan"):
/* TEXT PLANS */
SET SHOWPLAN_ALL ON; --TURNS ON Estimated Exececution Plan
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT *
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
SET SHOWPLAN_ALL OFF; --TURNS OFF Estimated Exececution Plan
SET STATISTICS PROFILE ON --TURNS ON Actual Exececution Plan
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT *
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
SET STATISTICS PROFILE OFF --TURNS OFF Actual Exececution Plan
We saw a bunch of data returned

We next moved on to XML Plans:
/* XML PLANS */
SET SHOWPLAN_XML ON; --TURNS ON Estimated Exececution Plan
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT *
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
SET SHOWPLAN_XML OFF; --TURNS OFF Estimated Exececution Plan
SET STATISTICS XML ON --TURNS ON Actual Exececution Plan
USE [AdventureWorks]
SELECT E.Title
,C.FirstName
,C.LastName
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
JOIN Person.Contact C ON E.ContactID = C.ContactID
WHERE E.ManagerID = 185
SET STATISTICS XML OFF --TURNS OFF Actual Exececution Plan
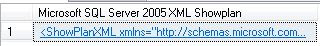
If you click on the returned XML it will open in Graphical Format. If you really want to see it in XML, when viewing a plan in Graphical Format, right click on a blank part of the screen and choose "Show Execution Plan XML"
I had two more pretty awesome queries to show you...the first was one that finds all "Missing Indexes" for all Databases.
SELECT TOP 10 SUBSTRING(mid.statement, 2, (CHARINDEX(']',mid.statement,1)-2)) AS DBName
,mid.statement
,migs.avg_total_user_cost
,migs.avg_user_impact
,migs.user_seeks
,migs.avg_total_user_cost * (migs.avg_user_impact / 100.0)
* (migs.user_seeks + migs.user_scans) AS improvement_measure
,'CREATE INDEX [missing_index_'
+ CONVERT (VARCHAR, mig.index_group_handle) + '_'
+ CONVERT (VARCHAR, mid.index_handle) + '_'
+ LEFT(PARSENAME(mid.statement, 1), 32) + ']' + ' ON ' + mid.statement
+ ' (' + ISNULL(mid.equality_columns, '')
+ CASE WHEN mid.equality_columns IS NOT NULL
AND mid.inequality_columns IS NOT NULL THEN ','
ELSE ''
END + ISNULL(mid.inequality_columns, '') + ')' + ISNULL(' INCLUDE ('
+ mid.included_columns
+ ')', '') AS create_index_statement
,migs.*
,mid.database_id
,mid.[object_id]
FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups mig
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats migs ON migs.group_handle = mig.index_group_handle
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_details mid ON mig.index_handle = mid.index_handle
WHERE migs.avg_total_user_cost * (migs.avg_user_impact / 100.0)
* (migs.user_seeks + migs.user_scans) > 1
ORDER BY migs.avg_total_user_cost * migs.avg_user_impact * (migs.user_seeks + migs.user_scans) DESC
And a query that can show you indexes which potentially are no longer used:
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM tempdb.dbo.sysobjects WHERE ID = OBJECT_ID(N'tempdb..#Temp_UnUsed_Indexes'))
BEGIN
DROP TABLE #Temp_UnUsed_Indexes
END
CREATE TABLE #Temp_UnUsed_Indexes
(
[Server] VARCHAR(100)
, DatabaseName VARCHAR(100)
, TableName VARCHAR(100)
, IndexName VARCHAR(100)
, is_primary_key BIT
, user_seeks INT
, user_scans INT
, user_lookups INT
, user_updates INT
, last_user_seek DATETIME
, last_user_scan DATETIME
, last_user_lookup DATETIME
, last_user_update DATETIME
, system_seeks INT
, system_scans INT
, system_lookups INT
, system_updates INT
, last_system_seek DATETIME
, last_system_scan DATETIME
, last_system_lookup DATETIME
, last_system_update DATETIME
)
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @Seeks INT = 30
,@Scans INT = 30
,@Lookups INT = 30
,@DBName VARCHAR(MAX)
,@SQL VARCHAR(MAX)
DECLARE ZCursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT NAME --select *
FROM sys.databases
WHERE owner_sid <> 0x01
AND is_read_only = 0
AND user_access = 0
ORDER BY name
OPEN ZCursor
FETCH NEXT FROM ZCursor INTO @DBName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
SET @SQL = '
USE [' + @DBName + ']
DECLARE @Seeks INT = ' + CAST(@Seeks AS VARCHAR(20)) + '
,@Scans INT = ' + CAST(@Scans AS VARCHAR(20)) + '
,@Lookups INT = ' + CAST(@Lookups AS VARCHAR(20)) + '
INSERT INTO #Temp_UnUsed_Indexes
SELECT @@SERVERNAME AS SERVER
, DB_NAME(DDIUS.database_id) AS DatabaseName
, OBJECT_NAME(DDIUS.object_id) AS TableName
, I.name AS IndexName
, I.is_primary_key AS is_primary_key
, DDIUS.user_seeks AS user_seeks
, DDIUS.user_scans AS user_scans
, DDIUS.user_lookups AS user_lookups
, DDIUS.user_updates AS user_updates
, DDIUS.last_user_seek AS last_user_seek
, DDIUS.last_user_scan AS last_user_scan
, DDIUS.last_user_lookup AS last_user_lookup
, DDIUS.last_user_update AS last_user_update
, DDIUS.system_seeks AS system_seeks
, DDIUS.system_scans AS system_scans
, DDIUS.system_lookups AS system_lookups
, DDIUS.system_updates AS system_updates
, DDIUS.last_system_seek AS last_system_seek
, DDIUS.last_system_scan AS last_system_scan
, DDIUS.last_system_lookup AS last_system_lookup
, DDIUS.last_system_update AS last_system_update
FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS DDIUS
JOIN sys.indexes AS I ON DDIUS.index_id = I.index_id AND DDIUS.object_id = I.object_id
WHERE database_id = DB_ID()
AND user_seeks <= @Seeks AND user_scans <= @Scans AND user_lookups <= @Lookups
--AND is_primary_key = 0
ORDER BY OBJECT_NAME(DDIUS.object_id), I.name
'
EXEC(@SQL)
-- PRINT @SQL
FETCH NEXT FROM ZCursor INTO @DBName
END
CLOSE ZCursor
DEALLOCATE ZCursor
SELECT *
FROM #Temp_UnUsed_Indexes
WHERE is_primary_key = 0
--AND user_seeks = 0 AND user_scans = 0 AND user_lookups = 0
--AND system_seeks = 0 AND system_scans = 0 AND system_lookups = 0
--AND DatabaseName NOT IN ('MOBILE')
ORDER BY [SERVER]
,DatabaseName
,TableName
,is_primary_key DESC
,IndexName
Remember that the numbers returned are since the last restart or DBCC FREEPROCCACHE so if you did that recently, don't trust these too much. Look at user_seeks, user_scans and user_lookups to see how often users have called this index. As always, do your research, this is a tool to help you identify probable indexes which might be unused.
I want to really thank Grant Fritchey, who literally wrote the book on Execution Plans, check out his stuff, he knows way more than I do about it.
http://www.simple-talk.com/author/grant-fritchey/
http://www.simple-talk.com/sql/performance/execution-plan-basics/
http://Scarydba.com/Resources
Lastly, if you are not already a member of PASS or PASSMN, please signup, it's free and we have monthly meetings where we discuss stuff and show code and talk about new stuff...it's a lot of fun. Also, PASS does something called 24 hours of pass, where they do 24 hourly webinars (over 2 days), for free!!! so sign up and check them out.
Please subscribe to my blog and follow me on Twitter (@EricZierdt).
Comment, or email me any questions.
Thursday, November 10, 2011
New SP_WHO2
USE [master]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
/*******************************
** Created By: Eric Zierdt **
** ericzierdt@gmail.com **
** ericemployed.blogspot.com **
*******************************/
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_whom]
AS
SET NOCOUNT ON
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM tempdb.dbo.sysobjects WHERE ID = OBJECT_ID(N'tempdb..#RawData'))
BEGIN
DROP TABLE #RawData
END
SELECT SPID
,UPPER(status) AS Status
,LogiName
,HostName
,CASE blocked
WHEN 0 THEN ''
ELSE CAST(blocked AS VARCHAR(5))
END AS BlockedBy
,Open_Tran
,DB_NAME(S.dbid) AS DBName
,CMD AS Command
,Last_Batch
,DATEDIFF(mi,last_batch,GETDATE()) AS RunTimeMins
,DATEDIFF(ss,last_batch,GETDATE()) AS RunTimeSecs
,CPU AS CPU_Time
,Physical_IO AS DiskIO
,Program_Name
,ST.text AS SQL_Text
INTO #RawData
FROM sys.sysprocesses AS S
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(S.sql_handle) ST
SELECT *
FROM #RawData R
WHERE spid <> @@SPID
AND status NOT IN ( 'background', 'sleeping' )
UNION
SELECT *
FROM #RawData AS RD
WHERE SPID IN (
SELECT BlockedBy
FROM #RawData AS RD2
WHERE RD2.BlockedBy <> ''
)
ORDER BY SPID
DROP TABLE #RawData
GO
Why are you doing a UNION you might ask? I'm doing it because I want to display only those SPIDS which are not set to "Sleeping" or "Background" status, however...if a SPID is blocked by another SPID, I'd like to display the blocking SPID as well. If I didn't do this and someone opens a transaction, updates records and doesn't close the transaction, their SPID's status will be Sleeping, so you will see that any spid trying to access the record(s) are blocked, but you won't know anything about the SPID doing the blocking.
I'd love feedback, is there something I should add to this to make it more useful? Please follow my blog and leave me some feedback.
P.s. because this is being placed in the master database and has the sp_ prefix you can call this from any database by just executing: "sp_whom" no need for exec or master.. or anything.
Friday, September 16, 2011
Deleting ZZ'd Objects
I decided to write a little script to search out the names of all my ZZ'd objects on a server (specifically User Tables, Procs and Agent Jobs) and store them in a temp table. Next I email the list to my development team offering them one last chance to save the object, and set about scripting it out. The script also creates a DROP script for you to run, so when you are ready, you can just run the script.
Works pretty well. Please comment below on how you facilitate removing old objects, is your method different from mine?
/*******************************
** Created By: Eric Zierdt **
** ericzierdt@gmail.com **
** ericemployed.blogspot.com **
*******************************/
IF object_id('tempdb..#ObjectList') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE #ObjectList
END
CREATE TABLE #ObjectList
(
DBName VARCHAR(100)
,ObjectName VARCHAR(100)
,ObjectType VARCHAR(2)
,ObjectType_Desc VARCHAR(100)
)
DECLARE @DBName AS VARCHAR(MAX)
,@SQL AS VARCHAR(MAX)
DECLARE ZCursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT name
FROM sys.databases
WHERE owner_sid <> '0x01'
ORDER BY name
OPEN ZCursor
FETCH NEXT FROM ZCursor
INTO @DBName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
PRINT 'Starting ' + @DBName
SET @SQL = 'USE [' + @DBName + ']
SELECT ''' + @DBName + ''' AS DBName, name,type,type_desc FROM sys.objects WHERE name LIKE ''%%zz%%'' ORDER BY CASE WHEN type = ''U'' THEN 1 ELSE 2 END, name
'
INSERT INTO #ObjectList
( DBName, ObjectName,ObjectType,ObjectType_Desc )
EXEC (@SQL)
FETCH NEXT FROM ZCursor
INTO @DBName
END
CLOSE ZCursor
DEALLOCATE ZCursor
USE msdb
INSERT INTO #ObjectList
( DBName, ObjectName,ObjectType,ObjectType_Desc )
SELECT 'msdb',name,'A','Agent Job'
FROM dbo.sysjobs
WHERE name LIKE '%%zz%'
-- SELECT * FROM #ObjectList
-- RUN THE CODE BELOW TO PRINT OUT THE DROP COMMANDS FOR THE OBJECTS
/*
DECLARE @DBName AS VARCHAR(MAX)
,@SQL AS VARCHAR(MAX)
,@ObjectName AS VARCHAR(MAX)
,@ObjectType AS VARCHAR(2)
,@Job_ID VARCHAR(257)
DECLARE DeleteCursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT DBName, ObjectName,ObjectType FROM #ObjectList --WHERE ObjectType = 'U'
OPEN DeleteCursor
FETCH NEXT FROM DeleteCursor
INTO @DBName,@ObjectName,@ObjectType
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
IF @ObjectType = 'U'
BEGIN
SET @SQL = 'DROP TABLE [' + @DBName + '].[dbo].[' + @ObjectName + ']
GO'
END
ELSE IF @ObjectType = 'P'
BEGIN
SET @SQL = 'USE [' + @DBName + ']
DROP PROCEDURE [dbo].[' + @ObjectName + ']
GO'
END
ELSE IF @ObjectType = 'A'
BEGIN
SELECT @Job_ID = job_id FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view WHERE name = N'' + @ObjectName + ''
SET @SQL = 'EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_delete_job @job_id=N''' + @Job_ID + ''', @delete_unused_schedule=1
GO'
END
ELSE
PRINT 'Unknown Object Type Found: [' + @ObjectType + ']'
PRINT @SQL
FETCH NEXT FROM DeleteCursor
INTO @DBName,@ObjectName,@ObjectType
END
CLOSE DeleteCursor
DEALLOCATE DeleteCursor
*/
Wednesday, June 8, 2011
Enable/Disable jobs
So one way to do this (arguably the faster way) is to open your job manager and highlight the invoke jobs and right-click and choose disable. But what if you have a few invokes disabled for one reason or another? You'll have to either remember which ones were disabled, or make a list, and make sure you don't re-enable those when you are done. Or, what if you want to wait for your current Invoke to end before you do the disable (not necessary, but what if), or you want to do it at a specific time of day?
I came up with a script that I put into two agent jobs to facilitate this. These can be scheduled and work pretty well.
The first job, creates a storage table, stores the id's for the enabled jobs, then disables them. (It checks to see if the job exists first and if so, error's out)
/*******************************
** Created By: Eric Zierdt **
** ericzierdt@gmail.com **
** ericemployed.blogspot.com **
*******************************/
IF OBJECT_ID('msdb.dbo.ActiveInvokeJobs') IS NULL
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE FRZ_ADMINDB.dbo.ActiveInvokeJobs (
job_id UNIQUEIDENTIFIER
, [Name] VARCHAR(255)
)
INSERT INTO msdb.dbo.ActiveInvokeJobs
( job_id, [Name])
SELECT job_id
,[Name]
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs S
WHERE enabled = 1
AND name LIKE '%invoke%'
UPDATE msdb.dbo.sysjobs
SET enabled = 0
WHERE job_id IN (
SELECT job_id
FROM msdb.dbo.ActiveInvokeJobs
)
END
ELSE
BEGIN
RAISERROR ('Storage Table Already Exists.',16,1);
END
The next agent job checks to see if the storage table exists, and if so enables the disabled jobs, then deletes the storage table.
/*******************************
** Created By: Eric Zierdt **
** ericzierdt@gmail.com **
** ericemployed.blogspot.com **
*******************************/
IF OBJECT_ID('msdb.dbo.ActiveInvokeJobs') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
UPDATE msdb.dbo.sysjobs
SET enabled = 1
WHERE job_id IN (
SELECT job_id
FROM msdb.dbo.ActiveInvokeJobs
)
DROP TABLE msdb.dbo.ActiveInvokeJobs
END
ELSE
BEGIN
RAISERROR ('Storage Table Does Not Exist.',16,1);
END






