Hello to everyone who finds my blog because of taking my SQLSaturday presentation on Execution Plans. As promised, I'm attaching my scripts.
What are Execution Plans?The definition I used in my presentation was:
"In simplest terms, Execution Plans are the steps that SQL Server takes in order to return the requested information."
How do I see Execution PlansFor Graphical Execution Plans there are a few ways:
In the Menu Bar choose Query and you can choose either Display Estimated Execution Plan or Include Actual Execution Plan.
Right Click Query Window
Control L (Estimated) / M (Actual)
Or the simplest way, use the two buttons
 Plan Type
Plan TypeGraphical, Text, XML
Gets more difficult to read as you go from left to right, but also get more info. i.e. Graphical is easier to read than is Text, which is easier to read than XML, but XML gives more info than Text, which in turn gives more info than Graphical.
Note: I've read that Microsoft is planning on deprecating Text Execution Plan
Permissionsysadmin, dbcreator or db_owner, or be granted the ShowPlan permission:
GRANT SHOWPLAN TO [username]
ReuseThe Optimizer stores plans so it can reuse them, this is removed on server restart or DBCC FREEPROCCACHE
The examples below use AdventureWorks and AdventureWorks2008, available at CodePlex
To start, please turn on Include Actual Execution Plan from any of the above described methods. Next run this query:
/* QUERY 1 */
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT *
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
In your results window, you will see a new tab called "Execution Plan", if you click on that, you should see the following. Hovering over the left most object will display the tool tip in this screenshot:
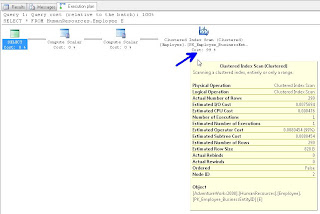
If you right click on any of the objects in this window you can choose Properties and get additional info. I traditionally read from right to left, but you can get important info like "Optimization Level" if you get the properties from the left most (select) object. The most common Optimization Levels are Trivial or Full. This is a trivial plan because there are no where clauses or joins, so the Optimizer can only get this data one way, doing a full table scan.
We discussed the difference between A Scan and a Seek. A Scan means that SQL Server needed to look at every record in the table, where as a Seek means that it can use an index to go directly to the record in question. We likened this to a phone book, if you are looking for the phone number and address for "Sam Smith", a Scan means you have to look at every page and every record even after it already finds a record for Sam Smith, whereas a Seek can go right to the S's at the top of the page and quickly go to the Sam Smith record and stop looking.
We discussed how typically, a scan performs worse than a seek. However if the table is small, and in some other instances, a Scan can be the best option.
Next we ran the following query:
/* QUERY 2 */
USE AdventureWorks
SELECT E.Title
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
WHERE E.EmployeeID = 185
And we saw an Clustered Index Seek this time.

Our next query:
/* QUERY 3 */
USE AdventureWorks
SELECT MiddleName
FROM Person.Contact
WHERE Phone LIKE '11%'
Showed us the "Missing Index" at the top of the Execution Plan
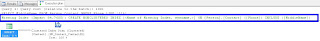
You can right click on this "Missing Index" text and "Missing Index Details" to have it open the suggested index in a new window.
We altered the index slightly (gave it a name and the WITH(Data_Compression=ROW) hint) and ran this:
USE [AdventureWorks]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [Contact_IX_Phone] ON [Person].[Contact]
(
[Phone]
)
INCLUDE
(
[MiddleName]
)
WITH(Data_Compression=ROW)
GO
We then re-ran Query 3 and saw that we now have an Index Seek.
For Query 4 we ran:
/* QUERY 4 */
USE AdventureWorks
SELECT E.Title
,C.FirstName
,C.LastName
,M.FirstName AS ManagerFirstName
,M.LastName AS ManagerLastName
,E.ManagerID
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
JOIN Person.Contact C ON E.ContactID = C.ContactID
JOIN Person.Contact M ON E.ManagerID = M.ContactID
WHERE E.ManagerID = 109
AND EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM Person.Contact AS C2
WHERE E.ContactID = C2.ContactID
)
Which showed us a Clustered Index Scan on HumanResources.Employee
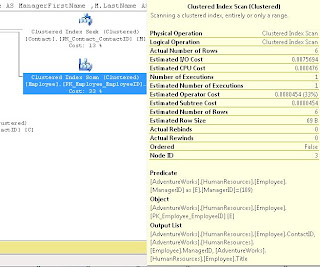
It didn't state a missing index so we discussed how to come up with our own index.
We started by noticing that ContactID and ManagerID were both being Joined, and that ManagerID was in the WHERE clause, so we created an index on that, also we used INCLUDE (Title) because Title was in the select List:
USE [AdventureWorks]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [HR-Employee_IX_EZ1] ON [HumanResources].[Employee]
(
[ContactID] ASC, [ManagerID] ASC
)
INCLUDE ( [Title])
WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF, ONLINE = ON, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION=ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
We did discuss some of the WITH parts, like the use of ONLINE = ON as a hint to try to make this index without causing any locking if possible.
After we ran this, we noted that the Index Scan still existed; we discussed that because the ContactID wasn't part of the WHERE, it should go in the INCLUDE. After making this change and re-running the index we saw it change to a Index Seek (note I'm using the DROP_EXISTING = ON here rather than the DROP statement I used in class).
USE [AdventureWorks]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [HR-Employee_IX_EZ1] ON [HumanResources].[Employee]
(
[ManagerID] ASC
)
INCLUDE ( [ContactID], [Title])
WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = ON, ONLINE = ON, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION=ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
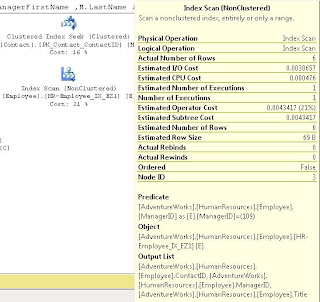
We noted that the when we hover over the Employee object in the above screen shots, that it the Estimated I/O Cost dropped from 0.0075 to 0.00386 after we converted from a SCAN to a SEEK and the Estimated Operator Cost changed from .008 to .004 We acknowledged that these numbers seem small, but if this table explodes and becomes very large, we would expect to see these go up and seeing the costs cut in half is a good thing.
For Query 5 we let the audience try to determine what was wrong and needed to be changed:
/* QUERY 5 */
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT SOH.AccountNumber
,S.Name AS StoreName
,SOH.OrderDate
,P.Name AS ProductName
,SOD.OrderQty
,SOD.UnitPrice
,SOD.LineTotal
FROM Sales.SalesOrderHeader SOH
JOIN Sales.SalesOrderDetail SOD ON SOH.SalesOrderID = SOD.SalesOrderID
JOIN Sales.Customer C ON SOH.CustomerID = C.CustomerID
JOIN Sales.Store S ON C.StoreID = S.BusinessEntityID
JOIN Production.Product P ON SOD.ProductID = P.ProductID
We had a big Execution Plan, we discussed that you can click on the [+] symbol at the bottom left of the window to help scroll around:
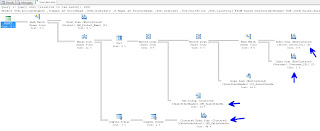
We all agreed that the Index Scan's had to go. We also introduced the "Key Lookup" object. I discussed how Key Lookups are not good, and indicate that the Optimizer couldn't get the key from the index. After looking at the query, we decided to add a number of indexes:
USE [AdventureWorks2008]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [SalesOrderHeader_I01] ON [Sales].[SalesOrderHeader]
(
[SalesOrderID] ASC,
[CustomerID] ASC
)
INCLUDE
(
AccountNumber
,OrderDate
)
WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF, ONLINE = OFF
, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
USE [AdventureWorks2008]
GO
/****** Object: Index [AK_SalesOrderDetail_rowguid] Script Date: 09/23/2011 14:35:47 ******/
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [SalesOrderDetail_I01] ON [Sales].[SalesOrderDetail]
(
SalesOrderID ASC
)
INCLUDE
(
ProductID
, OrderQty
,UnitPrice
,LineTotal
)
WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF
, ONLINE = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
USE [AdventureWorks2008]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [Customer_I01] ON [Sales].[Customer]
(
[CustomerID] ASC)
INCLUDE (
[StoreID]
)WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF, ONLINE = OFF
, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
USE [AdventureWorks2008]
GO
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [Store_I01] ON [Sales].[Store]
(
[BusinessEntityID] ASC
)
INCLUDE
(
Name
)
WITH (STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, DROP_EXISTING = OFF, ONLINE = OFF
, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
This did seem to help, when we compared the Estimated I/O's and CPU's but we still were seeing SCANS.
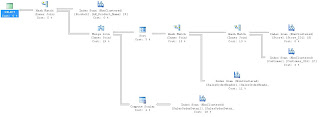
We scratched our heads and then realized that we didn't have a WHERE clause, so we were pulling every record possible. We added:
WHERE SOH.SalesOrderID = 22
and our Execution Plan looked much, much better.
By this time, I think you can figure out what needs to be done for Query 6:
/* QUERY 6 */
SELECT LineTotal, OrderQty
FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail s
JOIN Production.Product p ON s.ProductID = p.ProductID
WHERE CarrierTrackingNumber = '4911-403C-98'
Next I showed this query which returns all the Cached plans that SQL Server has ready to go:
SELECT [cp].[refcounts]
, [cp].[usecounts]
, [cp].[objtype]
, [st].[dbid]
, [st].[objectid]
, [st].[text]
, [qp].[query_plan]
FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans cp
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text ( cp.plan_handle ) st
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan ( cp.plan_handle ) qp ;
Then we moved on to looking at Execution Plans returned as Text (Note remember to turn off "Include Actual Execution Plan"):
/* TEXT PLANS */
SET SHOWPLAN_ALL ON; --TURNS ON Estimated Exececution Plan
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT *
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
SET SHOWPLAN_ALL OFF; --TURNS OFF Estimated Exececution Plan
SET STATISTICS PROFILE ON --TURNS ON Actual Exececution Plan
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT *
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
SET STATISTICS PROFILE OFF --TURNS OFF Actual Exececution Plan
We saw a bunch of data returned

We next moved on to XML Plans:
/* XML PLANS */
SET SHOWPLAN_XML ON; --TURNS ON Estimated Exececution Plan
USE AdventureWorks2008
SELECT *
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
SET SHOWPLAN_XML OFF; --TURNS OFF Estimated Exececution Plan
SET STATISTICS XML ON --TURNS ON Actual Exececution Plan
USE [AdventureWorks]
SELECT E.Title
,C.FirstName
,C.LastName
FROM HumanResources.Employee E
JOIN Person.Contact C ON E.ContactID = C.ContactID
WHERE E.ManagerID = 185
SET STATISTICS XML OFF --TURNS OFF Actual Exececution Plan
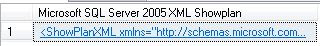
If you click on the returned XML it will open in Graphical Format. If you really want to see it in XML, when viewing a plan in Graphical Format, right click on a blank part of the screen and choose "Show Execution Plan XML"
I had two more pretty awesome queries to show you...the first was one that finds all "Missing Indexes" for all Databases.
SELECT TOP 10 SUBSTRING(mid.statement, 2, (CHARINDEX(']',mid.statement,1)-2)) AS DBName
,mid.statement
,migs.avg_total_user_cost
,migs.avg_user_impact
,migs.user_seeks
,migs.avg_total_user_cost * (migs.avg_user_impact / 100.0)
* (migs.user_seeks + migs.user_scans) AS improvement_measure
,'CREATE INDEX [missing_index_'
+ CONVERT (VARCHAR, mig.index_group_handle) + '_'
+ CONVERT (VARCHAR, mid.index_handle) + '_'
+ LEFT(PARSENAME(mid.statement, 1), 32) + ']' + ' ON ' + mid.statement
+ ' (' + ISNULL(mid.equality_columns, '')
+ CASE WHEN mid.equality_columns IS NOT NULL
AND mid.inequality_columns IS NOT NULL THEN ','
ELSE ''
END + ISNULL(mid.inequality_columns, '') + ')' + ISNULL(' INCLUDE ('
+ mid.included_columns
+ ')', '') AS create_index_statement
,migs.*
,mid.database_id
,mid.[object_id]
FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups mig
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats migs ON migs.group_handle = mig.index_group_handle
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_details mid ON mig.index_handle = mid.index_handle
WHERE migs.avg_total_user_cost * (migs.avg_user_impact / 100.0)
* (migs.user_seeks + migs.user_scans) > 1
ORDER BY migs.avg_total_user_cost * migs.avg_user_impact * (migs.user_seeks + migs.user_scans) DESC
And a query that can show you indexes which potentially are no longer used:
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM tempdb.dbo.sysobjects WHERE ID = OBJECT_ID(N'tempdb..#Temp_UnUsed_Indexes'))
BEGIN
DROP TABLE #Temp_UnUsed_Indexes
END
CREATE TABLE #Temp_UnUsed_Indexes
(
[Server] VARCHAR(100)
, DatabaseName VARCHAR(100)
, TableName VARCHAR(100)
, IndexName VARCHAR(100)
, is_primary_key BIT
, user_seeks INT
, user_scans INT
, user_lookups INT
, user_updates INT
, last_user_seek DATETIME
, last_user_scan DATETIME
, last_user_lookup DATETIME
, last_user_update DATETIME
, system_seeks INT
, system_scans INT
, system_lookups INT
, system_updates INT
, last_system_seek DATETIME
, last_system_scan DATETIME
, last_system_lookup DATETIME
, last_system_update DATETIME
)
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @Seeks INT = 30
,@Scans INT = 30
,@Lookups INT = 30
,@DBName VARCHAR(MAX)
,@SQL VARCHAR(MAX)
DECLARE ZCursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT NAME --select *
FROM sys.databases
WHERE owner_sid <> 0x01
AND is_read_only = 0
AND user_access = 0
ORDER BY name
OPEN ZCursor
FETCH NEXT FROM ZCursor INTO @DBName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
SET @SQL = '
USE [' + @DBName + ']
DECLARE @Seeks INT = ' + CAST(@Seeks AS VARCHAR(20)) + '
,@Scans INT = ' + CAST(@Scans AS VARCHAR(20)) + '
,@Lookups INT = ' + CAST(@Lookups AS VARCHAR(20)) + '
INSERT INTO #Temp_UnUsed_Indexes
SELECT @@SERVERNAME AS SERVER
, DB_NAME(DDIUS.database_id) AS DatabaseName
, OBJECT_NAME(DDIUS.object_id) AS TableName
, I.name AS IndexName
, I.is_primary_key AS is_primary_key
, DDIUS.user_seeks AS user_seeks
, DDIUS.user_scans AS user_scans
, DDIUS.user_lookups AS user_lookups
, DDIUS.user_updates AS user_updates
, DDIUS.last_user_seek AS last_user_seek
, DDIUS.last_user_scan AS last_user_scan
, DDIUS.last_user_lookup AS last_user_lookup
, DDIUS.last_user_update AS last_user_update
, DDIUS.system_seeks AS system_seeks
, DDIUS.system_scans AS system_scans
, DDIUS.system_lookups AS system_lookups
, DDIUS.system_updates AS system_updates
, DDIUS.last_system_seek AS last_system_seek
, DDIUS.last_system_scan AS last_system_scan
, DDIUS.last_system_lookup AS last_system_lookup
, DDIUS.last_system_update AS last_system_update
FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS DDIUS
JOIN sys.indexes AS I ON DDIUS.index_id = I.index_id AND DDIUS.object_id = I.object_id
WHERE database_id = DB_ID()
AND user_seeks <= @Seeks AND user_scans <= @Scans AND user_lookups <= @Lookups
--AND is_primary_key = 0
ORDER BY OBJECT_NAME(DDIUS.object_id), I.name
'
EXEC(@SQL)
-- PRINT @SQL
FETCH NEXT FROM ZCursor INTO @DBName
END
CLOSE ZCursor
DEALLOCATE ZCursor
SELECT *
FROM #Temp_UnUsed_Indexes
WHERE is_primary_key = 0
--AND user_seeks = 0 AND user_scans = 0 AND user_lookups = 0
--AND system_seeks = 0 AND system_scans = 0 AND system_lookups = 0
--AND DatabaseName NOT IN ('MOBILE')
ORDER BY [SERVER]
,DatabaseName
,TableName
,is_primary_key DESC
,IndexName
Remember that the numbers returned are since the last restart or DBCC FREEPROCCACHE so if you did that recently, don't trust these too much. Look at user_seeks, user_scans and user_lookups to see how often users have called this index. As always, do your research, this is a tool to help you identify probable indexes which might be unused.
I want to really thank Grant Fritchey, who literally wrote the book on Execution Plans, check out his stuff, he knows way more than I do about it.
http://www.simple-talk.com/author/grant-fritchey/
http://www.simple-talk.com/sql/performance/execution-plan-basics/
http://Scarydba.com/Resources
Lastly, if you are not already a member of PASS or PASSMN, please signup, it's free and we have monthly meetings where we discuss stuff and show code and talk about new stuff...it's a lot of fun. Also, PASS does something called 24 hours of pass, where they do 24 hourly webinars (over 2 days), for free!!! so sign up and check them out.
Please subscribe to my blog and follow me on Twitter (@EricZierdt).
Comment, or email me any questions.











